Nicotinamide Riboside, an NAD precursor and supplement, reduces liver damage caused by sepsis
Abstract
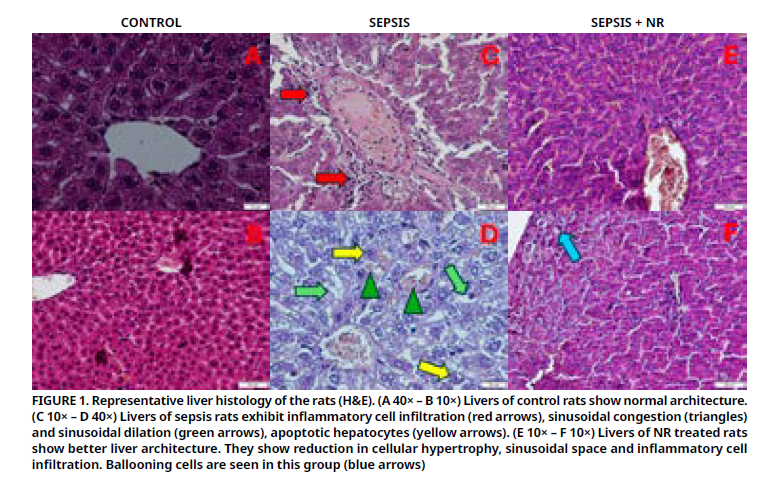
Sepsis leads to liver failure and eventually death. The supplement nicotinamide riboside is an antioxidant and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide precursor. This study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic effect effect of nicotinamide riboside on liver injury in a rat sepsis model induced by cecal ligation and perforation. 21 rats were divided into 3 groups: control, sepsis and sepsis+ nicotinamide riboside group. Cecal ligation and perforation applied to sepsis and sepsis + nicotinamide riboside groups. Nicotinamide riboside applied to sepsis + nicotinamide riboside group orally (200 mg·kg-1) 1 hour (h) before and 12 h after cecal ligation and perforation. 24 h after cecal ligation and perforation, rats sacrified. Histopathological and biochemical parameters were analyzed. Nicotinamide riboside treatment resulted in a decrease in high levels of aspartate and alanine aminotransferases, creatine, and ceruloplasmin. Serum albumin, calcium, and amylase levels were decreased in sepsis group and increased in sepsis + nicotinamide riboside group (P<0.05). However, no significant differences of uric acid, sodium, magnesium and chloride levels were seen between the groups. The liver structrure that injured because of sepsis were ameliorated histologically. Superoxide dismutase levels were low in sepsis group but elevated in sepsis + nicotinamide riboside group (P<0.05). Malondialdehyde levels were high in sepsis group but elevated in sepsis + nicotinamide riboside group (P<0.05). Nicotinamide riboside mitigated liver tissue damage in septic rats. It corrected the impaired oxidant-antioxidant balance and some serum parameters. This might be evidence of the ameliorative effect of nicotinamide riboside in liver. Nonetheless, new investigations should be held in the future to understand deeply the mechanism.
Downloads
References
Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy S, Moneim AEA. Ziziphus spina-christi leaf extract pretreatment inhibits liver and spleen injury in a mouse model of sepsis via anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammopharmacology [Internet]. 2018; 26:779–791. doi: https://doi.org/qq45
Woznica EA, Inglot M, Woznica RK, Lysenko L. Liver dysfunction in sepsis. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. [Internet]. 2018; 27(4):547–551. doi: https://doi.org/ghn5qm
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, Levy MM, Marshall JC, Martin GS, Opal SM, Rubenfeld GD, van der Poll T, Vincent JL, Angus DC. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). J. Am. Med. Assoc. [Internet]. 2016; 315(8):801–810. doi: https://doi.org/gdrcdh
Cao T, Ni R, Ding W, Ji X, Fan GC, Zhang Z, Peng T. Nicotinamide mononucleotide as a therapeutic agent to alleviate multi-organ failure in sepsis. J. Transl. Med. [Internet]. 2023; 21:883. doi: https://doi.org/qq47
Shi H, Han W, Shi H, Ren F, Chen D, Chen Y, Duan Z. Augmenter of liver regeneration protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury by promoting autophagy in mice. Oncotarget [Internet]. 2017; 8:12637–12648. doi: https://doi.org/f9k6sb
Esposito S, De Simone G, Boccia G, De Caro F, Pagliano P. Sepsis and septic shock: new definitions, new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. [Internet]. 2017; 10:204–212. doi: https://doi.org/gg328p
Hong G, Zheng D, Zhang L, Ni R, Wang G, Fan GC, Lu Z, Peng T. Administration of nicotinamide riboside prevents oxidative stress and organ injury in sepsis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. [Internet]. 2018; 123:125–137. doi: https://doi.org/gdtn4r
Ye M, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Xie R, Tong Y, Sauer JD, Gong S. NAD(H)-loaded nanoparticles for efficient sepsis therapy via modulating immune and vascular homeostasis. Nat. Nanotechnol. [Internet]. 2022; 17:880–890. doi: https://doi.org/gqbx88
Trammell SAJ, Yu L, Redpath P, Migaud ME, Brenner C. Nicotinamide riboside is a major NAD+ precursor vitamin in cow milk. J. Nutr. [Internet]. 2016; 146(5):957–963. doi: https://doi.org/f8kgjq
Kang H, Park YK, Lee JY. Nicotinamide riboside attenuates inflammation and oxidative stress by activating sirtuin-1 in alcohol-stimulated macrophages. Lab. Investig. [Internet]. 2021; 101(9):1225–1237. doi: https://doi.org/gqpxj8
Liu A, Wang W, Fang H, Yang Y, Jiang X, Liu S, Hu J, Hu Q, Dahmen U, Dirsch O. Baicalein protects against polymicrobial sepsis-induced liver injury via inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2015; 748:45–53. doi: https://doi.org/f6x8q3
Hamity MV, White SR, Blum C, Gibson-Corley KN, Hammond DL. Nicotinamide riboside relieves paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy and enhances suppression of tumor growth in tumor-bearing rats. Pain [Internet]. 2020; 161(10):2364–2375. doi: https://doi.org/qq49
Yener MD, Çolak T, Özsoy ÖD, Eraldemir FC. Alterations in catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase and malondialdehyde levels in serum and liver tissue under stress conditions. Istanb. Tip Fak. Derg. [Internet]. 2024; 87(2):145–152. doi: https://doi.org/qq5b
Muftuoglu MAT, Aktekin A, Ozdemir NC, Saglam A. Liver injury in sepsis and abdominal compartment syndrome in rats. Surg. Today [Internet]. 2006; 36:519–524. doi: https://doi.org/d6spxt
Zhu Z, Chambers S, Bhatia M. Suppressing the substance P-NK1R signalling protects mice against sepsis-associated acute inflammatory injury and ferroptosis in the liver and lungs. Antioxidants [Internet]. 2024; 13(3):300. doi: https://doi.org/qq5c
Cerrah S, Cadirci E, Okcu N, Deveci O. The determination of the protective role of sildenafil administration in rats with sepsis-induced liver injury. Turk. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. [Internet]. 2023; 29(2):133–139. doi: https://doi.org/qq5d
Liu X, Yang X, Han L, Ye F, Liu M, Fan W, Zhang K, Kong Y, Zhang J, Shi L, Chen Y, Zhang X, Lin S. Pterostilbene alleviates polymicrobial sepsis-induced liver injury: possible role of SIRT1 signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. [Internet]. 2017; 49:50–59. doi: https://doi.org/gbp58c
Peng X, Dai C, Liu Q, Li J, Qiu J. Curcumin attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice via modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway. Molecules [Internet]. 2018; 23(1):215. doi: https://doi.org/g77c74
Sakhuja P. Pathology of alcoholic liver disease, can it be differentiated from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? World J. Gastroenterol. [Internet]. 2014; 20(44):16474–16479. doi: https://doi.org/f6r9b4
Turck D, Castenmiller J, de Henauw S, Hirsch-Ernst KI, Kearney J, Knutsen HK, Maciuk A, Mangelsdorf I, McArdle HJ, Naska A, Pelaez C, Pentieva K, Siani A, Thies F, Tsabouri S, Vinceti M. Safety of nicotinamide riboside chloride as a novel food and bioavailability of nicotinamide from this source, in the context of Directive 2002/46/EC. EFSA J. [Internet]. 2019; 17(8):e05775. doi: https://doi.org/qq5r
Bonilla DA, Kreider RB, Stout JR, Forero DA, Kerksick CM, Roberts MD, Rawson ES. Metabolic basis of creatine in health and disease: a bioinformatics-assisted review. Nutrients [Internet]. 2021; 13(4):1238. doi: https://doi.org/gs8wg4
Nedel W, Deutschendorf C, Portela LVC. Sepsis-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: a narrative review. World J. Crit. Care Med. [Internet]. 2023; 12(3):139–152. doi: https://doi.org/qq5t
Casciola R, Leoni L, Cuffari B, Pecchini M, Menozzi R, Colecchia A, Ravaioli F. Creatine supplementation to improve sarcopenia in chronic liver disease: facts and perspectives. Nutrients [Internet]. 2023; 15(4):863. doi: https://doi.org/qq5s
Xu L, Han G. Research progress in pharmacokinetics of phosphocreatine, a cardioprotective agent with dual antiplatelet activity. Ann. Vasc. Med. Res. [Internet]. 2023; 10(4):1173. doi: https://doi.org/qq5v
Yoshino J, Baur JA, Imai SI. NAD+ intermediates: the biology and therapeutic potential of NMN and NR. Cell Metab. [Internet]. 2018; 27(3):513–528. doi: https://doi.org/gc7pkf
Klimova N, Long A, Kristian T. Nicotinamide mononucleotide alters mitochondrial dynamics by SIRT3-dependent mechanism in male mice. J. Neurosci. Res. [Internet]. 2019; 97(8):975–990. doi: https://doi.org/ggts79
Arslan NP, Akpinar Z, Aybek H, Doymus M, Asilkan-Kaldik G, Esim N, Taskin M. NAD+ precursors mitigate reproductive defects: limitations and possible solutions. Reprod. Toxicol. [Internet]. 2025; 138:109067. doi: https://doi.org/qq5w
Xie N, Zhang L, Gao W, Huang C, Huber PE, Zhou X, Li C, Shen G, Zou B. NAD+ metabolism: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. [Internet]. 2020; 5:227. doi: https://doi.org/ghrs66
Chaari A, Hakim KA, Rashed N, Bousselmi K, Kauts V, Etman M, Casey WF. Factors associated with increased pancreatic enzymes in septic patients: a prospective study. J. Intensive Care [Internet]. 2017; 5:44. doi: https://doi.org/qq5x
Tonai K, Katayama S, Koyama K, Imahase H, Nunomiya S. Association between hypomagnesemia and serum lactate levels in patients with sepsis. J. Anesth. Analg. Crit. Care [Internet]. 2024; 4:23. doi: https://doi.org/qq5z
Suetrong B, Pisitsak C, Boyd JH, Russell JA, Walley KR. Hyperchloremia is associated with acute kidney injury in severe sepsis. Crit. Care [Internet]. 2016; 20:315. doi: https://doi.org/gjvkcb
Han Y, Duan J, Chen M, Huang S, Zhang B, Wang Y, Liu J, Li X, Yu W. Relationship between serum sodium level and sepsis-induced coagulopathy. Front. Med. [Internet]. 2023; 10:1324369. doi: https://doi.org/qq52
He W, Huang L, Luo H, Zang Y, An Y, Zhang W. Hypocalcemia in sepsis: subcellular distribution of Ca2+ in septic rats and LPS·TNF-1-α-treated HUVECs. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. [Internet]. 2020; 14:908–917. doi: https://doi.org/gpg7c9
Saravi B, Goebel U, Hassenzahl LO, Jung C, David S, Feldheiser A, Stopfkuchen-Evans M, Wollborn J. Capillary leak and endothelial permeability in critically ill patients: a current overview. Intensive Care Med. Exp. [Internet]. 2023; 11:96. doi: https://doi.org/qq53
Soeters PB, Wolfe RR, Shenkin A. Hypoalbuminemia: pathogenesis and clinical significance. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. [Internet]. 2019; 43(2):181–193. doi: https://doi.org/gk45fg
Hayashi N, Yamaguchi S, Rodenburg F, Wong SY, Ujimoto K, Miki T, Iba T. Multiple biomarkers of sepsis identified by time-lapse proteomics. PLoS One [Internet]. 2019; 14(9):e0222403. doi: https://doi.org/grkr9p
Linder MC. Ceruloplasmin and other copper binding components of blood plasma and their functions: an update. Metallomics [Internet]. 2016; 8(9):887–905. doi: https://doi.org/gpdntz
Neşelioğlu S, Oğuz EF, Erel Ö. Development of a new Colorimetric, Kinetic and automated ceruloplasmin ferroxidase activity measurement method. Antioxidants [Internet]. 2022; 11(11):2187. doi: https://doi.org/qq54
Copyright (c) 2026 Zeliha Yetim

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


















