Hepatoprotective effect of Thymus vulgaris L. Extract against Paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in Oryctolagus cuniculus rabbits
Abstract
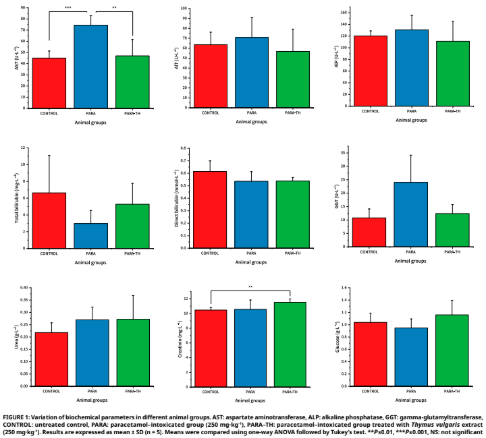
This study investigated the hepatoprotective effect of Thymus vulgaris L. against paracetamol-induced liver injury in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Fifteen male rabbits were randomly divided into three groups: untreated control, paracetamol- intoxicated (250 mg·kg-1), and paracetamol-intoxicated treated with T. vulgaris extract (250 mg·kg-1). Clinical parameters remained within normal limits across groups. Biochemical analyses revealed significant increases in aspartate aminotransferase and gamma- glutamyltransferase in the paracetamol-intoxicated group, while treatment with T. vulgaris markedly reduced these elevations, restoring values close to controls. Other biochemical markers, renal indices (urea, creatinine), and hematological parameters showed no significant changes, indicating that hepatic function was primarily affected. Histological examination confirmed these findings: livers of the paracetamol-intoxicated group exhibited trabecular disorganization, vacuolization, and necrosis, whereas thyme-treated animals showed largely preserved architecture with attenuated lesions. Renal tissue remained unaltered in all groups. These results demonstrate that T. vulgaris exerts a partial protective effect by limiting paracetamol-induced hepatocellular damage, without altering hematological or renal profiles, supporting its potential as a natural adjuvant against drug-induced hepatotoxicity.
Downloads
References
Prescott LF. Paracetamol: past, present, and future. Am. J. Ther. [Internet]. 2000; 7(2):143–147. Available from: https://goo.su/GbOlUdY DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00045391-200007020-00011
Larson AM. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Clin. Liver Dis. [Internet]. 2007; 11(3):525–548. doi: https://doi.org/chs54c DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2007.06.006
Ramachandran A, Jaeschke H. Mechanisms of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and their translation to the human pathophysiology. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2017; 3(Suppl1):157–169. doi: https://doi.org/gbkdv4
Jaeschke H, Ramachandran A. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Paradigm for understanding mechanisms of drug–induced liver injury. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2024; 19:453–478. doi: https://doi.org/gthwhc DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-051122-094016
James LP, Mayeux PR, Hinson JA. Acetaminopheninduced hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab. Dispos. [Internet]. 2003; 31(12):1499–1506. doi: https://doi.org/dr8r5w DOI: https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.31.12.1499
Athersuch TJ, Antoine DJ, Boobis AR, Coen M, Daly AK, Possamai L, Nicholson JK, Wilson ID. Paracetamol metabolism, hepatotoxicity, biomarkers and therapeutic interventions: a perspective. Toxicol. Res. 2018; 7(3):347–357. doi: https://doi.org/gmwbzq DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tx00340d
Jaeschke H, McGill MR, Ramachandran A. Oxidant stress, mitochondria, and cell death mechanisms in drug– induced liver injury: Lessons learned from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab. Rev. [Internet]. 2012; 44(1):88–106. doi: https://doi.org/fxmp3w DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/03602532.2011.602688
Ramlawi M, Marti C, Sarasin F. Intoxication aiguë au paracetamol [Acute paracetamol poisoning]. Rev. Med. Suisse. 2013; 9(394):1478–1482. French. doi: https://doi.org/qnxh DOI: https://doi.org/10.53738/REVMED.2013.9.394.1478
McGill MR, Jaeschke H. Metabolism and disposition of acetaminophen: recent advances in relation to hepatotoxicity and diagnosis. Pharm. Res. [Internet]. 2013; 30(9):2174– 2187.doi: https://doi.org/f47pj3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-1007-6
Fontana RJ. Acute liver failure including acetaminophen overdose. Med. Clin. North Am. [Internet]. 2008; 92(4):761– 794. doi: https://doi.org/c3pqnt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2008.03.005
Craig DGN, Bates CM, Davidson JS, Martin KG, Hayes PC, Simpson KJ. Overdose pattern and outcome in paracetamolinduced acute severe hepatotoxicity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2011; 71(2):273–282. doi: https://doi.org/fwptwq DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03819.x
Lee WM. Acetaminophen (APAP) hepatotoxicity—Isn’t it time for APAP to go away? J. Hepatol. 2017; 67(6):1324–1331. doi: https://doi.org/gcmcjx DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.07.005
Michalopoulos GK. Hepatostat: liver regeneration and normal liver tissue maintenance. Hepatology. 2017; 65(4):1384–1392. doi: https://doi.org/f9xffv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28988
Bhushan A, Apte U. Liver regeneration after acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Am. J. Pathol. 2019; 189(4):719–729. doi: https://doi.org/gnn98d DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.12.006
Ni HM, Williams JA, Jaeschke H, Ding WX. Zonated induction of autophagy and mitochondrial spheroids limits acetaminophen–induced necrosis in the liver. Redox Biol. 2013; 1(1):427–432. doi: https://doi.org/qnxj DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2013.08.005
Antoine DJ, Williams DP, Kipar A, Jenkins RE, Regan SL, Sathish JG, Kitteringham NR, Park BK. High–mobility group box–1 protein and keratin–18, circulating serum proteins informative of acetaminophen–induced necrosis and apoptosis in vivo. Toxicol Sci. 2009; 112(2):521–531. doi: https://doi.org/d6zbhv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfp235
Antoine DJ, Dear JW, StarkeyLewis PS, Platt V, Coyle J, Masson M, Thanacoody RH, Gray AJ, Webb DJ, Moggs JG, Bateman DN, Goldring CE, Park BK. Mechanistic biomarkers provide early and sensitive detection of acetaminopheninduced acute liver injury at first presentation to hospital. Hepatology [Internet]. 2013; 58(2):777–787. doi: https://doi.org/qm3v DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26294
Girish C, Pradhan SC. Drug development for liver diseases: focus on picroliv, ellagic acid and curcumin. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2008; 22(6):623–632. doi: https://doi.org/c7hb4f DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00618.x
Fakurazi S, Sharifudin SA, Arulselvan P. Moringa oleifera hydroethanolic extracts effectively alleviate acetaminophen– induced hepatotoxicity in experimental rats through their antioxidant nature. Molecules 2012; 17(7):8334–8350. doi: https://doi.org/gbbf8g DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17078334
Singh A, Bhat TK, Sharma OP. Clinical biochemistry of hepatotoxicity. J. Clin. Toxicol. [Internet]. 2011; S4:1–19. doi: https://doi.org/qm3z
Adewusi EA, Afolayan AJ. A review of natural products with hepatoprotective activity. J. Med. Plants Res. [Internet]. 2010 [cited Sep 05, 2025]; 4(13):1318–1334. Available in: https://goo.su/IxJy7s
Soliman MM, Aldhahrani A, Metwally MMM. Hepatoprotective effect of Thymus vulgaris extract on sodium nitriteinduced changes in oxidative stress, antioxidant and inflammatory marker expression. Sci. Rep. [Internet]. 2021; 11:5747. doi: https://doi.org/qm32 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85264-9
Andrade JM, Faustino C, Garcia C, Ladeira D, Reis CP, Rijo P. Rosmarinus officinalis L.: An update review of its phytochemistry and biological activity. Future Sci. OA. [Internet]. 2018; 4(4):FSO283. doi: https://doi.org/gdfj76 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4155/fsoa-2017-0124
Pandey B, Baral R, Kaundinnyayana A, Panta S. Promising hepatoprotective agents from the natural sources: a study of scientific evidence. Egypt. Liver J. 2023; 13:14. doi: https://doi.org/qnxm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43066-023-00248-w
Nouioura G, Kettani T, Tourabi M, Elousrouti LT, Al Kamaly O, Alshawwa SZ, Shahat AA, Alhalmi A, Lyoussi B, Derwich E. The protective potential of Petroselinum crispum (Mill.) Fuss. on paracetamol–induced hepatio–renal toxicity and antiproteinuric effect: A biochemical, hematological, and histopathological study. Medicina [Internet]. 2023; 59(10):1814. doi: https://doi.org/qnxn DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59101814
Baponwa O, Amang AP, Mezui C, Koubala BB, Siwe GT, Vandi VL, Tan PV. Antioxidant mechanism of renal and hepatic failure prevention related to paracetamol overdose by the aqueous extract of Amblygonocarpus andongensis stem bark. BioMed Res. Int. [Internet]. 2022; 2022:1846558. doi: https://doi.org/qnxp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1846558
Şahin B, Karabulut S, Filiz AK, Özkaraca M, Gezer A, Akpulat HA, Ataseven H. Galium aparine L. protects against acetaminopheninduced hepatotoxicity in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. [Internet]. 2022; 366:110119. doi: https://doi.org/qnxq DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110119
Heard KJ. Acetylcysteine for acetaminophen poisoning. N. Engl. J. Med. [Internet]. 2008; 359(3):285–292. doi: https://doi.org/fjjbfj DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMct0708278
Ali M, Khan T, Fatima K, Ali QUA, Ovais M, Khalil AT, Ullah I, Raza A, Shinwari ZK, Idrees M. Selected hepatoprotective herbal medicines: evidence from ethnomedicinal applications, animal models, and possible mechanism of actions. Phytother. Res. [Internet]. 2018; 32(2):199–215. doi: https://doi.org/gb39tp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5957
Kazemifar AM, Hajaghamohammadi AA, Samimi R, Alavi Z, Abbasi E, Asl MN. Hepatoprotective property of oral silymarin is comparable to N–acetyl cysteine in acetaminophen poisoning. Gastroenterol. Res. [Internet]. 2012; 5(5):190–194. doi: https://doi.org/ggj5s7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.4021/gr463e
Sener G, Sehirli AO, AyanogluDulger G. Protective effects of melatonin, vitamin E and Nacetylcysteine against acetaminophen toxicity in mice: a comparative study. J. Pineal Res. [Internet]. 2003; 35(1):61–68. doi: https://doi.org/d9xcsw DOI: https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-079X.2003.00050.x
Sarhan MA, Selim KA, Roby MH, Khalel IK. Evaluation of antioxidant activity, total phenols and phenolic compounds in thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.), sage (Salvia officinalis L.) and marjoram (Origanum majorana L.) extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013; 43:827–831. doi: https://doi.org/pqqj DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.08.029
Rašković A, Pavlović N, Kvrgić M, Sudji J, Mitić G, Čapo I, Mikov M. Effects of pharmaceutical formulations containing thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) on carbon tetrachlorideinduced liver injury in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. [Internet]. 2015; 15:442.doi: https://doi.org/f748tf DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0966-z
Guesmi F, Tyagi AK, Bellamine H, Landoulsi A. Antioxidant machinery related to decreased MDA generation by Thymus algeriensis essential oilinduced liver and kidney regeneration. Biomed. Environ. Sci. [Internet]. 2016 [cited Sep 05, 2025]; 29(9):639–649. Available in: https://goo.su/0bzRXzf
Muhsin A, Naz D, Naseem S, Nazir S, Rahman SU, Khan S. Oxidative stress, hematological and histopathological alterations recovery by methanolic extract of Celtis occidentalis L. leaves in paracetamolinduced hepatic injury in rabbits. J. Health Rehabil. Res. [Internet]. 2024; 4(3):1–8. doi: https://doi.org/qnxv DOI: https://doi.org/10.61919/jhrr.v4i3.1487
Mazer M, Perrone J. Acetaminopheninduced nephrotoxicity: Pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. J. Med. Toxicol. [Internet]. 2008; 4(1):2–6.doi: https://doi.org/dbhdxc DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160941
Ahmed JH. A significant hepatotoxicity associated with paracetamol overdose in the absence of kidney injury in rabbits. Int. J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2014; 3(6):1043–1047. doi: https://doi.org/qm65 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5455/2319-2003.ijbcp20141216
Ali B, AlWabel NA, Shams S, Ahamad A, Khan SA, Anwar F. Essential oils used in aromatherapy: A systemic review. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. [Internet]. 2015; 5(8):601–611. doi: https://doi.org/gkdtkz DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.05.007
Nikolić M, Glamočlija J, Ferreira ICFR, Calhelha RC, Fernandes Â, Marković T, Marković D, Giweli AM, Soković M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial, antioxidant and antitumor activity of Thymus serpyllum L., Thymus algeriensis Boiss. & Reut and Thymus vulgaris L. essential oils. Ind. Crops Prod. [Internet]. 2014; 52:183–190. doi: https://doi.org/qnxw DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.10.006
Patil SM, Ramu R, Shirahatti PS, Shivamallu C, Amachawadi RG. A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacological aspects of Thymus vulgaris Linn. Heliyon [Internet]. 2021; 7(5):e07054. doi: https://doi.org/grjqr2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07054
SharifiRad M, Varoni EM, Iriti M, Martorell M, Setzer WN, del Mar Contreras M, Salehi B, SoltaniNejad A, Rajabi S, Tajbakhsh M, SharifiRad J. Carvacrol and human health: A comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. [Internet]. 2018; 32(9):1675–1687. doi: https://doi.org/gd9m4g DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6103
Mahran YF, Badr AM, Al–Kharashi LA, Alajami HN, Aldamry NT, Bayoumy NM, Elmongy EI, Soliman S. Thymol protects against 5–Fluorouracil–induced hepatotoxicity via the regulation of the Akt•GSK–1–3β pathway in In Vivo and In Silico experimental models. Pharmaceuticals [Internet]. 2024; 17(8):1094. doi: https://doi.org/qnx2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17081094
Rodriguez J, Ortuno C, Benedito J, Bon J. Optimization of the antioxidant capacity of thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) extracts: Management of the drying process. Ind. Crops Prod. [Internet]. 2013; 46:258–263. doi: https://doi.org/qnx3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.02.002
Abu–Darwish MS, Alu’datt MH, Al–Tawaha AR, Ereifej K, Almajwal A, Odat N, Khateeb W. Seasonal variation in essential oil yield and composition from Thymus vulgaris L. during different growth stages in the south of Jordan. Nat. Prod. Res. [Internet]. 2012; 26(14):1310–1317. doi: https://doi.org/d2kgcq DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2011.576344
Feraguena I, Aouzal B, Boulkenafet F, Maachia L, Nasr F A, Al–zharani M, Wadaan M A, Al–Mekhlafi F A. Phytochemical characterization and evaluation of the antioxidant, antimicrobial, and in vivo protective effects of Ulva lactuca extracts from the Algerian coast. S. Afr. J. Bot. [Internet]. 2025; 186:175–185. doi: https://doi.org/qnx4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2025.09.013
Ranneh Y, Bedir AS, Abu–Elsaoud AM, Al Raish S. Polyphenol intervention ameliorates non–alcoholic fatty liver disease: an updated comprehensive systematic review. Nutrients [Internet]. 2024; 16(23):4150. doi: https://doi.org/qnx5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234150