Physiological and health response of broiler chickens treated with a probiotic additive
Abstract
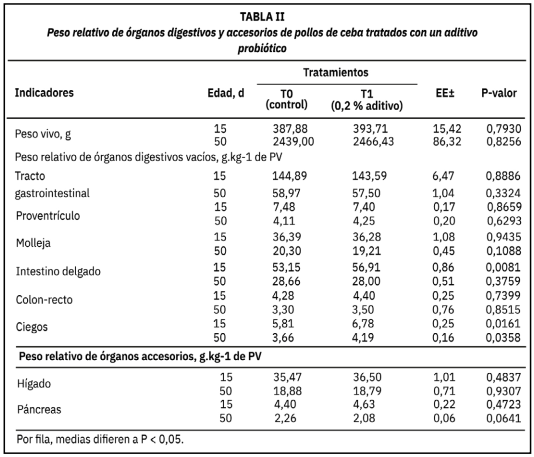
The aim was to determine the physiological and health response of broiler chickens treated with a probiotic additive. The experiment was carried out on an experimental poultry farm of Cevallos (Tungurahua, Ecuador), with 100 Cobb500 chickens, of both sexes, 1 day old and 41± 2 of live weight. The birds were distributed according to a completely randomized design in two treatments with five repetitions: control (T0) and 0.2 % of additive (T1). Each repetition was considered an experimental unit composed of 10 birds. In the evaluation of additive, eight animals per treatment are randomly selected, and morpho- physiological, histological and health indicators were determined. The relative weight of the small intestine of birds at 15 days of age to increase with the use of 0.2 % of the additive (53.15 vs. 56.91 g.kg- ¹; P = 0,0081). This effect was also found for the ceca at 15 and 50 days and the thymus at 15 days (3.22 vs. 4.77 g.kg-¹; P = 0,0005). Furthermore, at 50 days with the additive, the height and width of the villi, the villus height:crista depth ratio (4.19 vs. 5.25; P = 0.0473) and the absorptive surface area of the duodenum villi (0.68 vs. 1.04 mm²; P = 0.0006) increased, while the concentration of IgM was higher at 15 and 50 days. Beneficial variations were also observed in blood indicators such as total proteins, albumins and albumin/globulin ratio (P < 0.05). The results showed that the additive under study produces beneficial effects on the morphology of internal organs, modulates the immune response and improves intestinal health, which stimulates digestion and nutrient absorption. Therefore, it is demonstrated that the additive produced probiotic activity and could be used in poultry production.
Downloads
References
Shahbaz F, Muccee F, Shahab A, Safi SZ, Alomar SY, Qadeer A. Isolation and in vitro assessment of chicken gut microbes for probiotic potential. Front. Microbiol. [Internet]. 2024; 15:1278439. doi: https://doi.org/qj8f DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1278439
Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (FAO). Producción y productos avícolas. [Internet]. 2025 [citada 18 Mar 2025]. Disponible en: https://goo.su/27RMGho
Organización para la Cooperación y el Desarrollo Económicos-Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Alimentación y la Agricultura (OCDE/FAO) Perspectivas agrícolas 2017-2026. [Internet]. París: OECD Publishing; 2017. 154 p. doi: https://doi.org/gs5w
Jones PJ, Niemi J, Christensen JP, Tranter RB, Bennett RM. A review of the financial impact of production diseases in poultry production systems. Anim. Prod. Sci. [Internet]. 2019; 59(9):1585-1597. doi: https://doi.org/gmx9xv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/AN18281
Chica-Rosado SL, Cedeño-Pozo J, Barcia-Anchundia JX. Effect of organic acid in layers on productive parameters and water quality. Rev. Colomb. Cienc.Anim. Recia. [Internet]. 2021; 13(2):e868. doi: https://doi.org/qj8g DOI: https://doi.org/10.24188/recia.v13.n2.2021.868
Ashayerizadeh A, Jafarzadeh-Shirazi MR, Moradi HR, Kazemi K, Karimi-Akbarabadi Z, Jazi V. Effects of drinking water supplemented with apple vinegar, essential oils, or colistin sulfate on growth performance, blood lipids, antioxidant status, intestinal morphology, and gut microflora of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. [Internet]. 2025; 104(2):104801. doi: https://doi.org/qj8j DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2025.104801
Ahmed SK, Hussein S, Qurbani K, Ibrahim RH, Fareeq A, Mahmood KA, Mohamed MG. Antimicrobial resistance: Impacts, challenges, and future prospects. J. Med. Surgery Public Heal. [Internet]. 2024; 2:100081. doi: https://doi.org/g9wp6p DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.glmedi.2024.100081
Júpiter RA. Producción y comercialización de pollos en el Cantón La Libertad, provincia de Santa Elena. [Trabajo de Grado en Internet]. Santa Elena, Ecuador: Universidad Estatal Península de Santa Elena, Ecuador; 2021 [citada 19 Mar 2025]. 80 p. Disponible en: https://goo.su/RENkjQ
Sánchez AM, Vayas T, Mayorga F, Freire C. Sector avícola Ecuador. Observatorio Económico y Social de Tungurahua. [Internet]. Universidad Técnica de Ambato, Ecuador: Observatorio Económico y Social de Tungurahua. 2020 [citada 19 Mar 2025]. Disponible en: https://goo.su/4KH5g6
Guerrero-López JR, Valiño-Cabrera EC, Rodríguez-Sánchez B, García-Hernández Y, González-Puetate IR. Microbiological and chemical characteristics of a zootechnical additive obtained in Ecuador for its use in animal feeding. Cuban J. Agric. Sci. [Internet]. 2025 [citada 10 Sep 2025]; 59:e07. Disponible en: https://goo.su/6UzO9v
Agrocalidad. Guía de Buenas Prácticas Avícolas de la Agencia Ecuatoriana de Aseguramiento de la Calidad del Agro. Ecuador: Sistema Agrocalidad. [Internet]. 2020 [citada 20 Feb 2025]; 45 p. Disponible en: https://goo.su/oMPN
Cobb500 2015. Suplemento informativo sobre rendimiento y nutrición de pollos de engorde. [Internet]. 2015 [citada 19 Feb 2025]. Disponible en: https://goo.su/zYbxbl3
Bustamante-García D, Savón-Valdés LL, Iglesias EA, Caro-Ríos Y, Valiño-Cabrera EC, Valera-Rojas M, Martin-Nyachoti C, Mireles S. Chemical and microbiological characterization of a technological variant of Vitafert intended for animal production. Technical note. Cuban J. Agric. Sci. [Internet]. 2021; 55(2):e02. Disponible en: https://goo.su/yuBjvzA
Prakatur I, Miskulin M, Pavic M, Marjanovic K, Blazicevic V, Miskulin I, Domacinovic M. Intestinal morphology in broiler chickens supplemented with propolis and bee pollen. Animals. [Internet]. 2019; 9(6):301-312. doi: https://doi.org/qj8m DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9060301
Di Rienzo JA, Casanoves F, Balzarini MG, Gonzalez L, Tablada M, Robledo CW. Software libre InfoStat versión 2012. Argentina: Grupo InfoStat, FCA, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. [Internet]. 2012 [Recuperada 25 May 2025]. Disponible en: https://goo.su/ERJT
Fisher RA, Yates F. Statistical tables for biological, agricultural and medical research. 5th Edition. Edinburgh and London: Oliver and Boyd;1958. 138 p.
Chávez LA, López A, Parra JE. Crecimiento y desarrollo intestinal de aves de engorde alimentadas con cepas probióticas. Arch. Zootec. [Internet]. 2016; 65(249):5158. doi: https://doi.org/qj8n DOI: https://doi.org/10.21071/az.v65i249.441
Quevedo DM, Ochoa JE, Corredor JR, Pulecio SL. Effects of addition of probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae on intestinal histomorphology in broilers. Rev. Med. Vet. Zoot. [Internet]. 2020; 67(3):239-252. doi: https://doi.org/qj8p DOI: https://doi.org/10.15446/rfmvz.v67n3.93931
Soumeh EA, Coba-Cedeno AR, Niknafs S, Bromfield J, Hoffman LC. The efficiency of probiotics administrated via different routes and doses in enhancing production performance, meat quality, gut morphology, and microbial profile of broiler chickens. Animals. [Internet]. 2021; 11(12):3607. doi: https://doi.org/qj8q DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123607
SAvaín A, Kalam-Azad MdA, García Y, García Y, Martínez Y. Effects of Ganoderma lucidum powder on the growth performance, immune organ weights, cecal microbiology, serum immunoglobulins, and tibia minerals of broiler chickens. Vet. Sci. [Internet]. 2024; 11(12):675-686. doi: https://doi.org/qj8r DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11120675
Akram W, Aslam MA, Mehnaz S, Siddiq U, Zaman A, Qamar F, Ehtisham-ul-Haque S, Bukhari SFA, Sarfraz MA, Ullah MH. An overview of beneficiary effects of prebiotics and probiotics on animals. [Internet]. In: Farooqi SH, Aqib AI, Zafar MA, Akhtar T, Ghafoor N. (eds). Pakistan, Faisalabad: Unique Scientific Publishers. 2024. pp: 1-11. doi: https://doi.org/qj8s DOI: https://doi.org/10.47278/book.CAM/2024.197
Ceylan A, Saçakli P, Özgenç-Çinar Ö, Shazaib-Ramay M, Ahsan U, Harijaona JA, Bayraktaroglu AG, Manghebati F, Calik A. Effect of supplemental dietary phytogenic blends on growth performance, jejunal histomorphometry, and jejunal immunity of broiler chickens. Arch. Anim Breed. [Internet]. 2025; 68:13-26. doi: https://doi.org/qj8t DOI: https://doi.org/10.5194/aab-68-13-2025
Manyeula F, Sebola NA, Mabelebele M. Productive, internal organ and intestinal histomorphological characteristics of broiler chickens in response to dietary rapeseed meal: A meta-analysis. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. [Internet]. 2025; 109:211-222. doi: https://doi.org/qj8w DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.14040
Zhang C, Hao E, Chen X, Huang C, Liu G, Chen H, Wang D, Shi L, Xuan F, Chang D, Chen Y. Dietary fiber level improve growth performance, nutrient digestibility, immune and intestinal morphology of broilers from Day 22 to 42. Animals. [Internet]. 2023; 13(7):1227-1240. doi: https://doi.org/qj8x DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13071227
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO). Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. London Ontario, Canada: FAO/WHO.[Internet]. 2002 [citada 25 Oct 2019]. 11 p. Disponible en: https://goo.su/1zqxLBV
Kogut MH. The effect of microbiome modulation on the intestinal health of poultry. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. [Internet]. 2019; 250:32-40. doi: https://doi.org/gmzhr6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2018.10.008
Tabashsum Z, Peng M, Alvarado-Martinez Z, Aditya A, Bhatti J, Romo-Bravo P, Young A, Biswas D. Competitive reduction of poultry-borne enteric bacterial pathogens in chicken gut with bioactive Lactobacillus casei. Sci. Rep. [Internet]. 2020; 10:16259. doi: https://doi.org/qj8z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73316-5
Cano-Chauvell RD. Probiotics and the Microbiome: Mechanisms, Strain Selection, and the Future of Rational Formulation Design. An. Acad. Cienc. Cuba. [Internet]. 2024; 14(4):e1888. Disponible en: https://goo.su/b90rtWx
Jha R, Mishra P. Dietary fiber in poultry nutrition and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, gut health, and on the environment: a review. J. Anim Sci. Biotechnol. [Internet]. 2021; 12:51. doi: https://doi.org/qj83 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-021-00576-0
Röhe I, Zentek J. Lignocellulose as an insoluble fiber source in poultry nutrition: a review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. [Internet]. 2021; 12:82. doi: https://doi.org/qj84 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40104-021-00594-y
Martínez Y, Altamirano E, Ortega V, Paz P, Valdivié M. Effect of age on the immune and visceral organ weights and cecal traits in modern broilers. Animals. [Internet]. 2021; 11(3):845-858. doi: https://doi.org/qj85 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030845
Zhou H, Wu Y, Sun X, Yin D, Wang Y, Mahmood T, Yuan J. Effects of exogenous a-(1,4)-amylase on the utilization of corn starch and glucose metabolism in broiler chickens. Animal. [Internet]. 2021; 15(11):100396. doi: https://doi.org/qj86 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.animal.2021.100396
Sosa-Cossio D, García-Hernández Y, Dustet-Mendoza JC, García-Curbelo Y, Martínez-Pérez M, Sosa-Ceijas A, García-Quiñones D. Efecto del aditivo probiótico Lactobacillus pentosus LB-31 en pollos de ceba. Rev. MVZ Córdoba. [Internet]. 2021; 26(1):e2037. doi: https://doi.org/jkph DOI: https://doi.org/10.21897/rmvz.2037
Soren S, Mandal GP, Mondal S, Pradhan S, Mukherjee J, Banerjee D, Pakhira MC, Amla Mondal A, Nsereko V, Samanta I. Efficacy of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation product and probiotic supplementation on growth performance, gut microflora and immunity of broiler chickens. Animals. [Internet]. 2024; 14(6):866. doi: https://doi.org/qj87 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060866
He S, Yin Q, Xiong Y, Liu D, Hu H. Effects of dietary fumaric acid on the growth performance, immune response, relative weight and antioxidant status of immune organs in broilers exposed to chronic heat stress. Czech J. Anim. Sci. [Internet]. 2020; 65(3):104-113. doi: https://doi.org/gk8zq5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17221/13/2020-CJAS
Li J, Cheng Y, Chen Y, Qu H, Zhao Y, Wen C, Zhou Y. Dietary chitooligosaccharide inclusion as an alternative to antibiotics improves intestinal morphology, barrier function, antioxidant capacity, and immunity of broilers at early age. Animals. [Internet]. 2019; 9(8):493-504. doi: https://doi.org/gphggc DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani9080493
Alizadeh M, Bavananthasivam J, Shojadoost B, Astill J, Taha-Abdelaziz K, Alqazlan N, Boodhoo N, Shoja-Doost J, Sharif S. In ovo and oral administration of probiotic Lactobacilli modulate cell- and antibody-mediated immune responses in newly hatched chicks. Front. Immunol. [Internet]. 2021; 12:1-13. doi: https://doi.org/qj88 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.664387